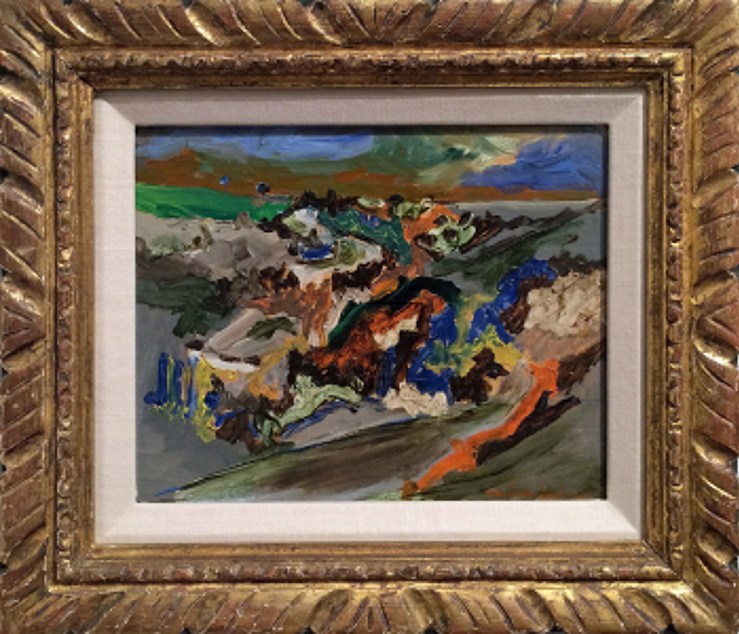
We discovered this still life at the preview of a Santa Fe estate sale. It was tucked in a dark upstairs corner of the house, far from the Picasso print and treasure trove of art books on prominent display in the living room. Lawrence lingered for a while to take in the flamboyant bouquet with its rich rosy tones. There was an excited glint in his eye.
A few months later, the painting has found a home under the glowing lights of our European art room. We know a lot more about it now than when it first caught Lawrence’s fancy. It’s attributed to Jean-Baptiste Monnoyer (1636-1699), a 17th century Franco-Flemish painter who wielded his brush for Louis XIV. Its siblings hang in some of France and England’s most famous estates.
Our adobe art abode is a very different venue, but this 300-year-old artwork gives us the opportunity to transport gallery visitors across the sea and through the ages. Look below to chase Monnoyer through the palaces where he left his mark, and don’t miss the painting’s debut at our opening for FOUR CENTURIES: European Art from 1600 to 1950 on Friday, June 13 from 5-7 pm.
Our first stop is the Hotel Lambert on the Ile Saint-Louis, site of Monnoyer’s first Parisian commission in 1650. The artist grew up in Lille, France and trained in Antwerp, but it was the lavish estates in and around Paris that claimed his considerable interior decorating talents. Monnoyer’s floral designs in the grand mansion would delight its many owners and guests for centuries to come, from a famous Polish political salon to Voltaire, Chopin, Balzac, Delacroix and Dali. Unfortunately, the Hotel Lambert was badly damaged in a 2013 fire and is under renovation.
Artist Charles Le Brun, who painted a series of renowned ceiling frescoes at the Hotel Lambert, brought Monnoyer along for a commission at Louis XIV’s Chateau de Marly. The (relatively) small country estate was the king’s escape from the more rigid world of Versailles, and aristocrats fiercely battled for a chance to stay there. Alas, the twelve pavilions that flanked the water and their intricately adorned interiors are long gone, but the commission launched Monnoyer into a new stratosphere.
Monnoyer worked with Le Brun once again on the ornamentation of the Palace of Versailles. For this and other high profile royal projects, he developed a style that was far removed from his training in the subdued still life painting techniques of the Low Countries. The bold, ornamental approach is in full force in our still life, recalling the spectacular garlands of flowers he painted on the ceiling of the Queen’s pavilion at the Chateau de Vincennes. Monnoyer also made reference sketches and etchings for French tapestry workshops, greatly influencing European decorative styles for years to come.
A commission from the Montagu House in London drew Monnoyer away from Paris in 1690. He adorned dozens of panels with fruits and vegetables and painted several portraits, some of which now reside in the state rooms of Northamptonshire’s Boughton House. The artist remained in England until his death in 1699, but his distinctly French style lived on in the artwork of two of his sons.
Make sure to attend the opening of our FOUR CENTURIES exhibition on Friday, June 13 from 5-7 pm, and follow us on Facebook, Twitter and Tumblr for daily gallery news.